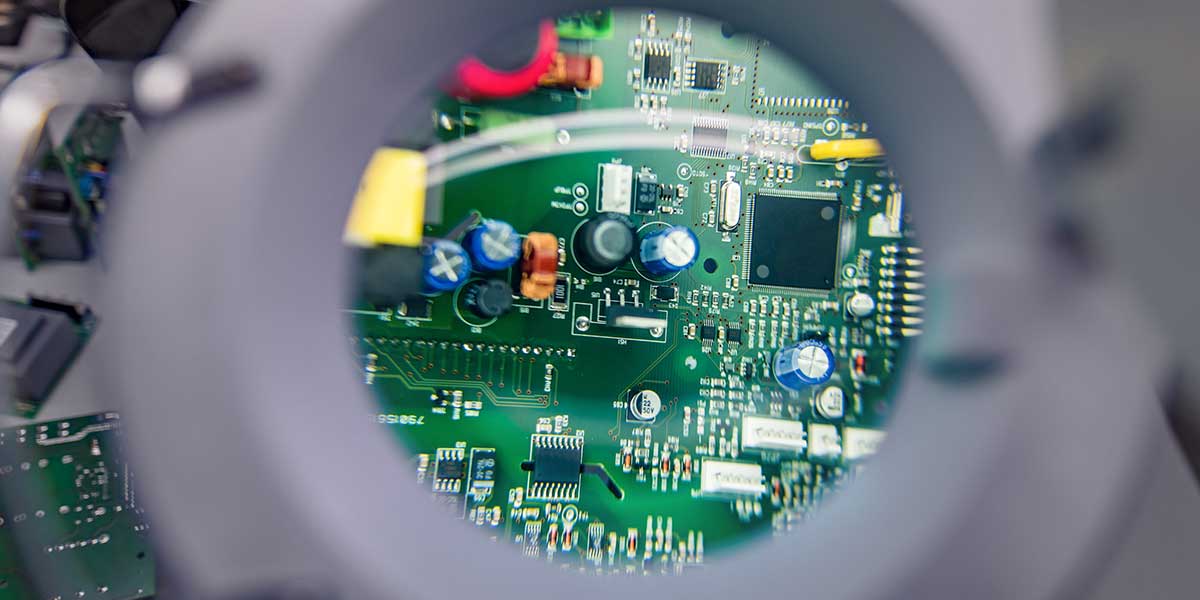
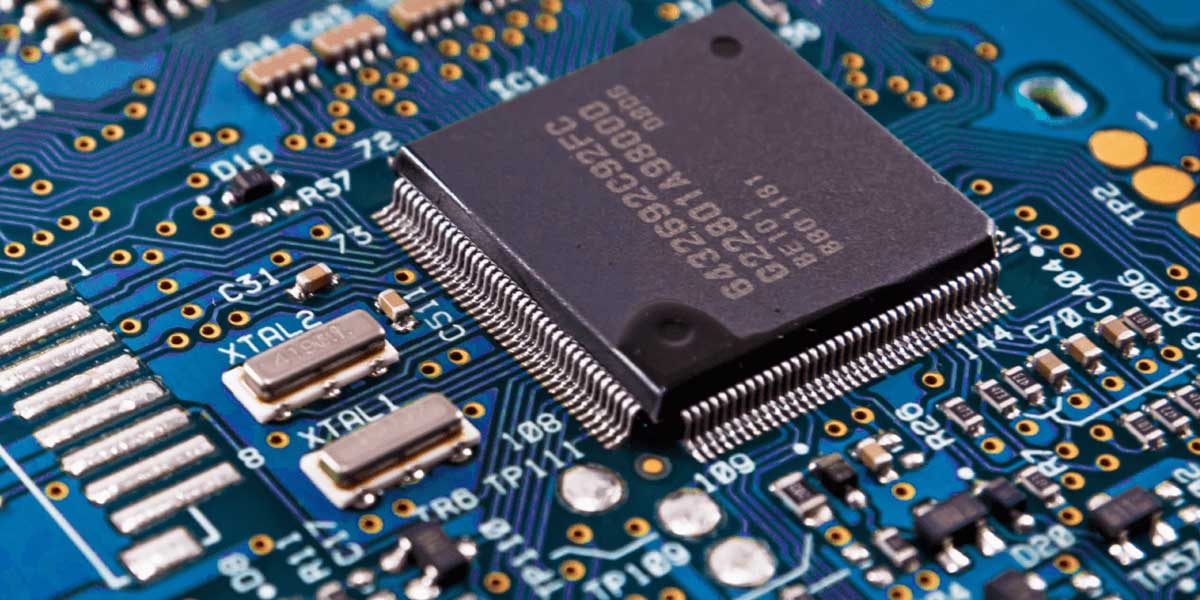
IPC-610 is a widely recognized standard in the printed circuit board (PCB) industry. It provides guidelines and requirements for the acceptability of electronic assemblies, including PCBs, during manufacturing and assembly processes. The standard covers various aspects of PCB production, such as component placement, soldering, cleanliness, and overall workmanship.
Here’s an example of content related to IPC-610 and PCB manufacturing:
Introduction
In the world of electronics manufacturing, the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) are of paramount importance. To ensure consistent quality and adherence to industry standards, the IPC-610 standard was established. IPC-610 sets the criteria for evaluating the acceptability of electronic assemblies, including PCBs, during different stages of production. This article aims to provide an overview of IPC-610 and its significance in PCB manufacturing.
1. IPC-610 Overview
IPC-610, also known as IPC-A-610, is a widely adopted standard developed by the Association Connecting Electronics Industries (IPC). It outlines the acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies based on visual inspection and workmanship standards. The standard defines various classes, each specifying different levels of acceptability for PCB assembly.
2. Classifications
IPC-610 categorizes electronic assemblies into three classes: Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3. Each class represents a different level of quality and reliability requirements. Class 1 is the least stringent, typically used for consumer products. Class 2 is for general-purpose electronics, while Class 3 is the highest level, reserved for applications with the most critical reliability requirements, such as aerospace and medical devices.
3. Acceptance Criteria
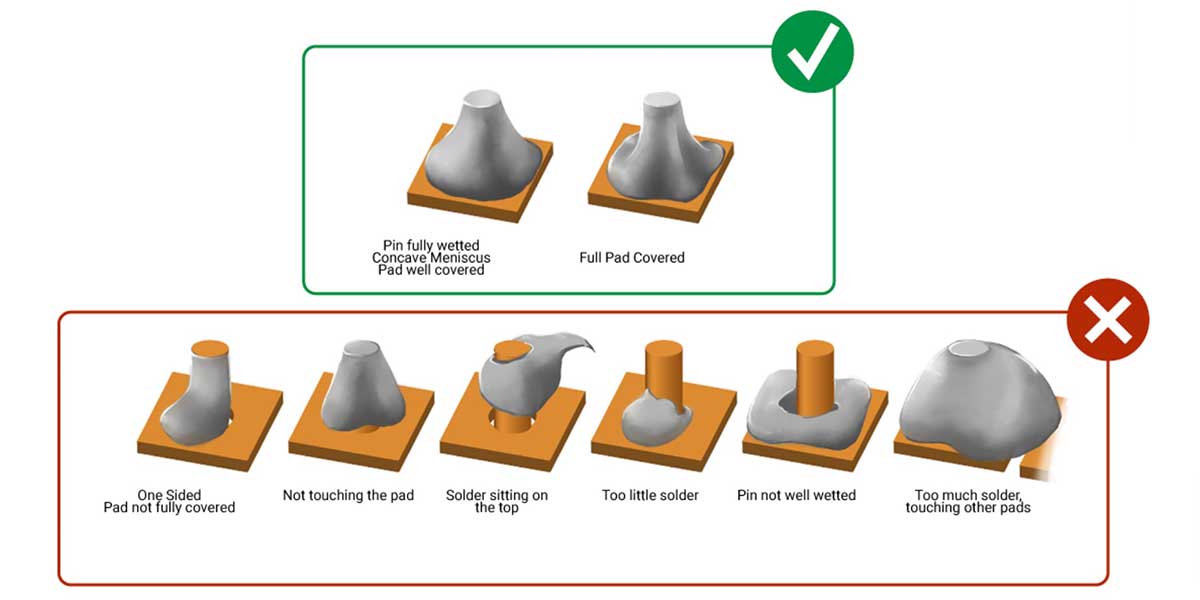
IPC-610 provides detailed guidelines for assessing the acceptability of various aspects of PCB manufacturing, including component placement, soldering, cleanliness, and overall workmanship. It covers a wide range of criteria, such as acceptable component spacing, solder joint conditions, conformal coating, cleanliness standards, and more.
4. Visual Inspection
Visual inspection plays a vital role in determining the compliance of a PCB assembly with IPC-610 standards. The standard provides visual examples and illustrations of acceptable and unacceptable conditions, aiding inspectors in making consistent and accurate assessments. Proper lighting, magnification tools, and trained inspectors are essential for reliable visual inspections.
5. Training and Certification
IPC-610 offers training programs and certification courses for individuals involved in PCB manufacturing and inspection. These training programs provide in-depth knowledge of the standard’s requirements and interpretations, ensuring consistent understanding and application across the industry.
Conclusion
IPC-610 is a crucial standard in the PCB manufacturing industry, providing guidelines for evaluating the acceptability of electronic assemblies. Adherence to IPC-610 ensures consistent quality, reliability, and workmanship, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and product performance. By following the standard’s guidelines and investing in training and certification, manufacturers can enhance their manufacturing processes and deliver high-quality PCB assemblies.
Please note that the example above is a general overview and does not cover all aspects of IPC-610. The actual standard document contains much more detailed information and should be consulted for precise requirements and guidelines.