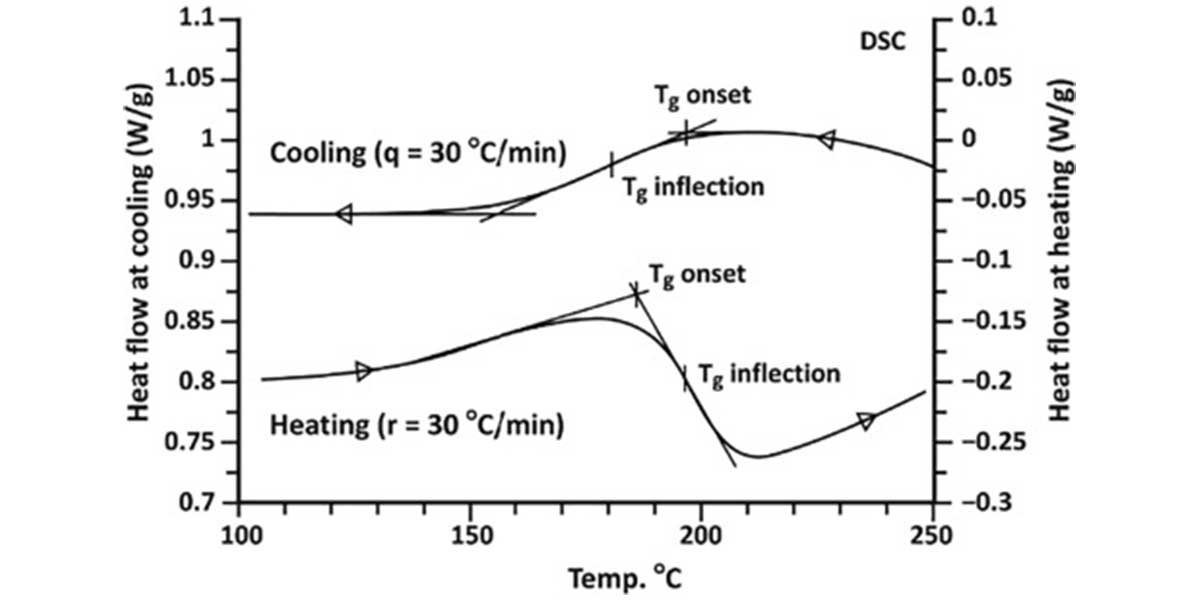
The TG value is an essential consideration in PCB fabrication because it determines the maximum temperature at which the PCB can operate reliably without undergoing significant changes in its mechanical and electrical properties. Operating the PCB above its glass transition temperature can lead to dimensional changes, warping, delamination, and reduced performance.
When selecting materials for PCB fabrication, it’s crucial to choose a substrate with a TG value that exceeds the expected operating temperatures of the PCB. This ensures that the board can withstand the thermal stress and environmental conditions it may encounter during its lifecycle. Higher TG values are typically preferred for applications where the PCB will be subjected to elevated temperatures, such as in high-power electronics or industrial environments.
By understanding the TG of the PCB substrate, designers and manufacturers can make informed decisions about material selection, stack-up design, and the overall reliability of the final product.
Some additional information about TG in PCB fabrication:
- Importance of TG: The glass transition temperature (TG) is a critical parameter in PCB fabrication because it determines the maximum temperature at which the PCB material retains its mechanical and electrical properties. Operating the PCB above its TG can lead to issues like dimensional changes, reduced structural integrity, and electrical performance degradation.
- TG and Material Selection: Different PCB materials have varying TG values. Common materials used in PCB fabrication include FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4), which has a TG of around 130-140°C, and high-temperature materials like polyimide or PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), which have higher TG values exceeding 200°C. Selecting a material with a suitable TG for the intended application is crucial to ensure the PCB’s reliability.
- Thermal Stress Considerations: PCBs can experience thermal stress due to factors such as temperature variations, heat generated by components, and external environments. If the operating temperature exceeds the TG of the PCB material, it can result in structural issues like warping, delamination, and solder joint failures. Therefore, designers must consider the expected operating temperature range and select materials with TG values that can withstand those conditions.
- Design Considerations: PCB designers need to consider the TG of the chosen material during the design phase. They must ensure that critical components, heat-generating elements, and high-temperature areas are appropriately placed on the board to manage heat dissipation and prevent localized temperature increases that could exceed the TG of the material.
- Reliability and Performance: By selecting a PCB material with a TG that exceeds the expected operating temperatures, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and performance of the final product. High-TG materials provide better dimensional stability, improved resistance to thermal stress, and reduced risk of performance degradation, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Testing and Certification: PCB manufacturers often perform tests, such as thermal cycling and solderability tests, to evaluate the reliability and performance of PCBs under different temperature conditions. Compliance with industry standards and certifications ensures that the PCBs can withstand the specified operating temperatures without significant degradation.
Understanding the TG of PCB materials and considering it during material selection, design, and testing stages is crucial to ensure the reliability, longevity, and performance of the PCB in various operating environments and temperature conditions.